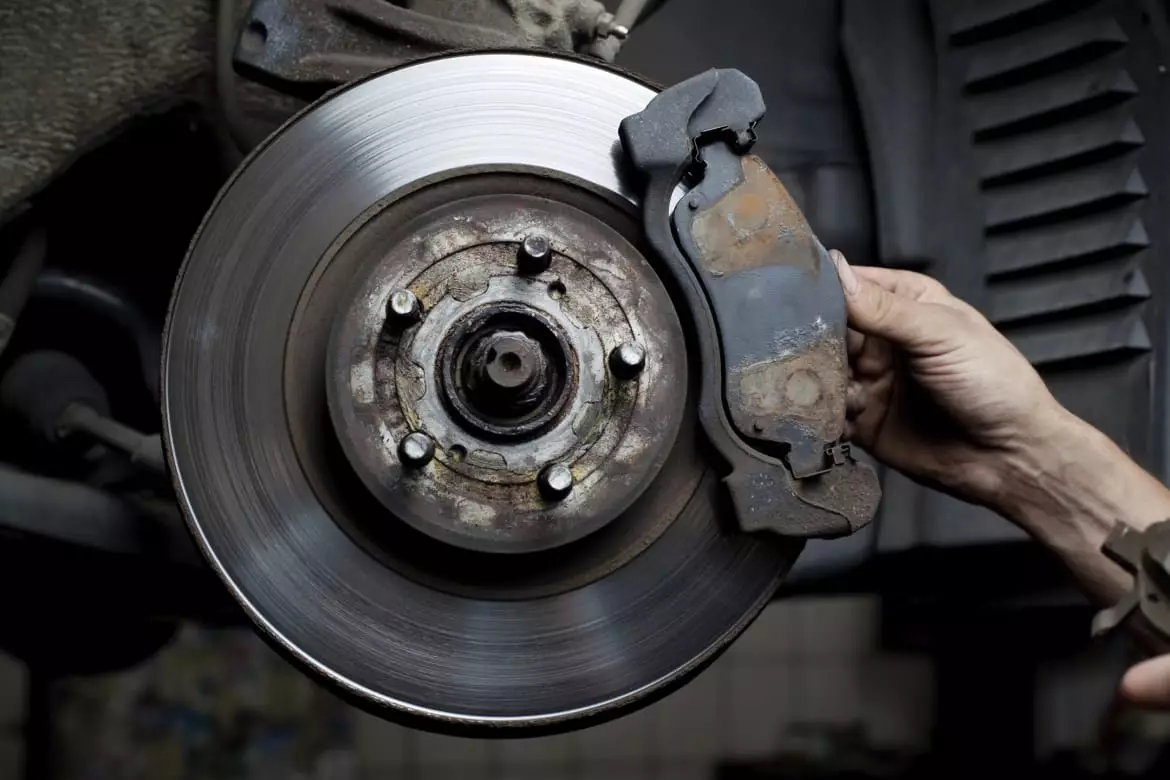
Routinely servicing your vehicle allows you to spot potential problems early and maximizes its longevity. But between scheduled maintenance intervals, certain symptoms act as clear indicators that your car requires attention from a technician. Identifying these warning signs of needed maintenance allows for addressing issues promptly before small problems balloon into major repairs.
This article covers the top signs of impending maintenance needs and how to diagnose them. We’ll examine common symptoms like warning lights, performance changes, noises, and smells pointing to underlying mechanical issues. Recognizing these clues allows taking action before permanent damage or breakdowns occur. Let’s explore what your car is trying to tell you when it’s feeling under the weather.
The Dreaded Check Engine Light
The check engine light (CEL) is your car’s key way of signaling a detected issue in the engine management system. While this amber engine-shaped light can illuminate temporarily from minor factors like a loose gas cap, it otherwise indicates a sensor or component malfunction needing diagnosis and repair.
Ignoring the CEL allows underlying issues to worsen through continued operation, potentially causing further degradation or secondary failures. It should never be disregarded.

Obtain the Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The CEL light itself does not identify the specific problem. It is simply an indicator of the onboard diagnostics system identifying a fault. To determine the cause, the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) must be pulled from the engine computer using an OBD2 code scanner.
Common trouble codes pointing to maintenance needs include:
- P0300-0306 – Misfiring cylinder
- P0420 – Catalytic converter efficiency below threshold
- P0171 – System too lean
- P0172 – System too rich
- P0440 – Evaporative emissions system leak
The specific DTCs present will direct further diagnostic steps to isolate the root issue.
CEL Causes Range from Benign to Serious
While a CEL can signify potentially major mechanical issues, minor maintenance oversights frequently trigger it as well:
- Loose or faulty gas cap resulting in evaporative emissions leak
- Failing oxygen sensor providing inaccurate readings
- Fouled spark plugs misfiring under load
- Broken ignition coil preventing proper cylinder firing
- Clogged fuel injector throwing off fuel trim
- Vacuum leaks through damaged hoses or gaskets
But the light also warns of more serious conditions like:
- Catalytic converter failure
- Early stages of head gasket leakage
- Turbo or supercharger issues
- Faulty mass airflow sensor skewing fuel mixture
So while some CEL causes may be cheap maintenance items, the light should never be casually dismissed as many factors can quickly escalate into costly repairs if ignored.
Rough Engine Idling- Signs Your Car Needs Maintenance
When your engine is fully warmed up but shakes and misfires at idle, it signals impending maintenance to address ignition or fuel delivery issues. The causes include:
Failing Ignition System Components
- Cracked ignition coil inability to properly fire spark plugs
- Worn or fouled spark plugs with inefficient firing in the cylinder
- Damaged plug wires leak voltage before reaching the plugs
Fuel System Problems
- Weak fuel pump unable to maintain optimum fuel rail pressure
- Clogged fuel injector disrupting spray pattern and atomization
- Contaminated or low-quality fuel skewing fuel mixture away from the ideal
Vacuum Leaks
- Damaged, loose, or disconnected PCV hoses and components
- Failed intake gasket allowing unmetered air into the engine
- Other ruptured vacuum hoses upset airflow ratios

Rough idling allows diagnosing and addressing the underlying fuel or ignition problem before catalytic converter and engine damage occurs from prolonged rough running.
Loss of Power Under Acceleration
When pressing the accelerator pedal fails to deliver the expected acceleration and power, improper fuel or air delivery is likely to diminish engine output. Causes include:
Fuel System Issues
- Weak fuel pump unable to maintain optimum pressure
- Clogged fuel injectors disrupting proper spray patterns
- Contaminated low-quality gasoline
- Excessive fuel pressure regulator leakage
Air Restrictions
- Loose or damaged air intake components allow unmetered air leaks
- Clogged air filter unable to flow adequate air for power demands
- Failing mass air flow sensor providing inaccurate readings
Don’t just compensate for lack of power by pressing the gas harder. Identify restrictions or defects reducing power production and correct them promptly to avoid catalyst damage from misfires or running rich.
Unusual Noises From a Wheel Area

When a grinding, squealing, or clicking noise arises from a wheel area that increases with vehicle speed, inspect the following potential culprits:
Brake Issues
- Worn brake pads lacking material to make solid contact with rotors
- Brake pad hardware vibrating against rotors due to looseness
- Glazed rotors preventing pads from gripping adequately under braking
Wheel Bearing Failure
- Damaged or worn wheel hub bearing allowing excessive play
- Bearing beginning to seize preventing smooth rotation
Other Suspension Issues
- Dry, worn, or damaged control arm ball joint rattling under load
- Stabilizer link end bushings deteriorating and clicking
Isolate the noise by jacking up one wheel at a time and testing components. Addressing such noises promptly before catastrophic bearing or brake failures occur reduces repair costs and driving hazards.
Burning Smell Coming From Vehicle
Unusual burning odors emanating from the engine bay, cabin, or wheel areas almost always indicate fluid leaks onto hot components. Be sure to safely pull over and diagnose immediately when noticing burning smells:
Engine Bay Sources
- Coolant leaks onto hot components from failed hoses, water pumps, head gaskets, or heater cores. Confirm via coolant pressure testing.
- Oil leaks onto exhaust components like the muffler or catalytic converter from compromised gaskets, seals, or cracked housings. Inspect for obvious oil residue traces.
- Transmission fluid leaks from damaged cooler lines, gaskets, or seal surfaces.
Cabin Sources
- Coolant from leaking heater core dripping onto heat exchangers. Visually inspect core and airflow for contamination.
- Motor oil makes contact with hot exhaust components or catalytic converters. Look for blue smoke from the oil after warming up.
Wheel Areas
- Brake fluid dripping onto hot brake rotors due to hydraulic system leaks at calipers, lines, or master cylinders.
Pinpoint leaks urgently to prevent fluid loss hazards like steering failure or brake failure. Identify and repair the source – don’t just top up fluids temporarily.
Additional Maintenance Reminder Symptoms
Beyond major issues like warning lights, performance problems, and leaks, monitor your vehicle for these additional signs of pending maintenance needs:
- Intermittent check engine light illumination indicating pending failure
- Stiff or unresponsive steering suggests low-power steering fluid
- Gear shifts are not crisp indicating low transmission fluid
- Squeaking suspension on bumps and turns pointing to worn bushings
- Fading headlights signaling aged bulbs and foggy lenses
- Uneven tire wear aligned due to misaligned wheels or bad struts
- Pulsing brake pedal showing warped rotors needing resurfacing
Learn your vehicle’s normal sounds and behaviors so you quickly notice deviations that signal needed maintenance. Following factory-recommended inspection intervals is also key. But your car provides sensory clues between services about issues arising. Monitor warning lights, performance, noises, smells, and component functionality closely to maximize longevity through prompt maintenance. Addressing small issues early prevents big bills down the road.